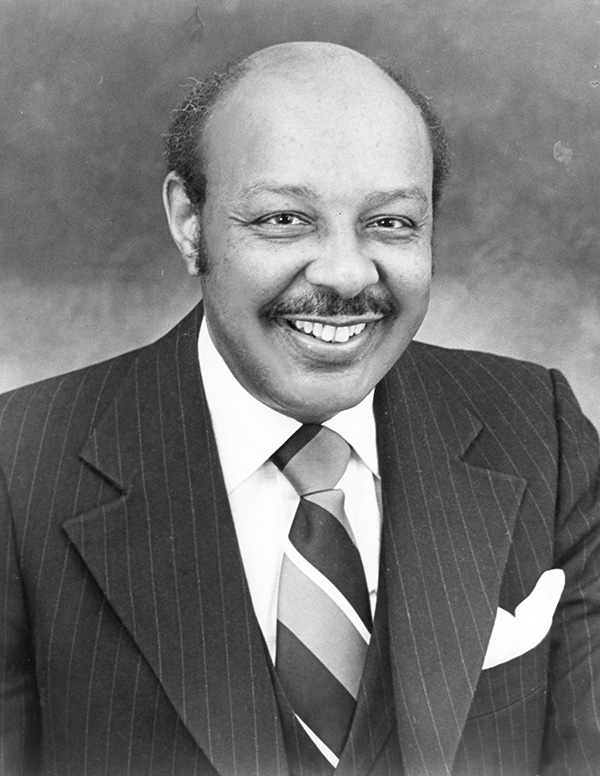
Born in Cleveland, Stokes and his brother Carl B. Stokes lived in one of the first federally funded housing projects, the Outhwaite Homes. Stokes served in the U.S. Army from 1943 to 1946. After attending Western Reserve University and Cleveland-Marshall College of Law, Stokes began practicing law in Cleveland in 1953. Stokes argued the seminal “stop and frisk” case of Terry v. Ohio before the United States Supreme Court in 1968. Later in 1968, he was elected to the House, representing the 21st District of Ohio on Cleveland’s East Side. He shifted to the newly created 11th District, covering much of the same area following a 1992 redistricting. Stokes served 15 terms in total, retiring in 1999.

Stokes’ tenure in the House of Representatives included service on the House Appropriations Committee, where he was influential in bringing revenue to Cleveland. He was particularly interested in veterans’ issues and secured funds for health-care facilities for veterans in Cleveland. In the 1970s, Stokes served as Chairman of the House Select Committee on Assassinations, charged with investigating the murders of President John F. Kennedy and civil rights leader Martin Luther King, Jr. Stokes also served on the House committee that investigated the Iran-Contra Affair.
Stokes’ brother, Carl B. Stokes, was the first African American mayor of a large American city. His daughter, Angela Stokes, serves as a Cleveland Municipal Court judge while another, Lori Stokes, is a journalist with WABC-TV New York. His son, Chuck Stokes, is also a journalist with WXYZ-TV in Detroit. Funk and soul musician Rick James was a cousin. Stokes and his wife, Jay, have seven grandchildren. Stokes practiced law in Cleveland, Ohio and Washington, D.C. Many buildings throughout the country have been named in Stokes honor including: Howard University’s medical library, the Cleveland Public Library’s main building expansion, GCRTA’s Windermere station Louis Stokes Station at Windermere, and the greater Cleveland area Veteran’s hospital was renamed the Louis Stokes Cleveland Department of Veteran Affairs Medical Center.
In 2006, the Western Reserve Historical Society opened an exhibition on the lives of Congressman Stokes and his brother titled “Carl and Louis Stokes: From the Projects to Politics”. The exhibit opened in November 2006 and closed in September 2008. The exhibit used photographs, manuscript collections, and personal items to showcase Louis Stokes’ rise from the Outhwaite homes, his legal career, and his Congressional service.
The former Congressman was inducted into the Karamu House Hall of Fame in 2007 for his contributions to the continued legacy of Cleveland’s black settlement house and theatre. Stokes was also a member of the Cleveland Alumni Chapter of Kappa Alpha Psi Fraternity, Inc. Stokes was a partner in the law firm of Squire, Sanders & Dempsey, with offices in Cleveland and Washington.
Later life and Death
Stokes retired in 2012 as Senior Counsel in the law firm of Squire, Sanders & Dempsey, with offices in Cleveland and Washington On July 20, 2015, it was reported that Stokes had both brain cancer and lung cancer. Stokes died on August 18, 2015, at his home in Cleveland from lung and brain cancer at the age of 90.